Microscope
A microscope is a special tool that helps us look at things that are too tiny to see with just our eyes — like cells, bacteria, or grains of pollen.
Imagine looking at a drop of pond water and seeing tiny living creatures swimming around. That’s the power of a microscope!
🧠 Why Use a Microscope?
- To study cells, the tiny building blocks of life.
- To observe fine details of objects, like insect wings or leaf veins.
- To carry out experiments in biology, chemistry, and more.
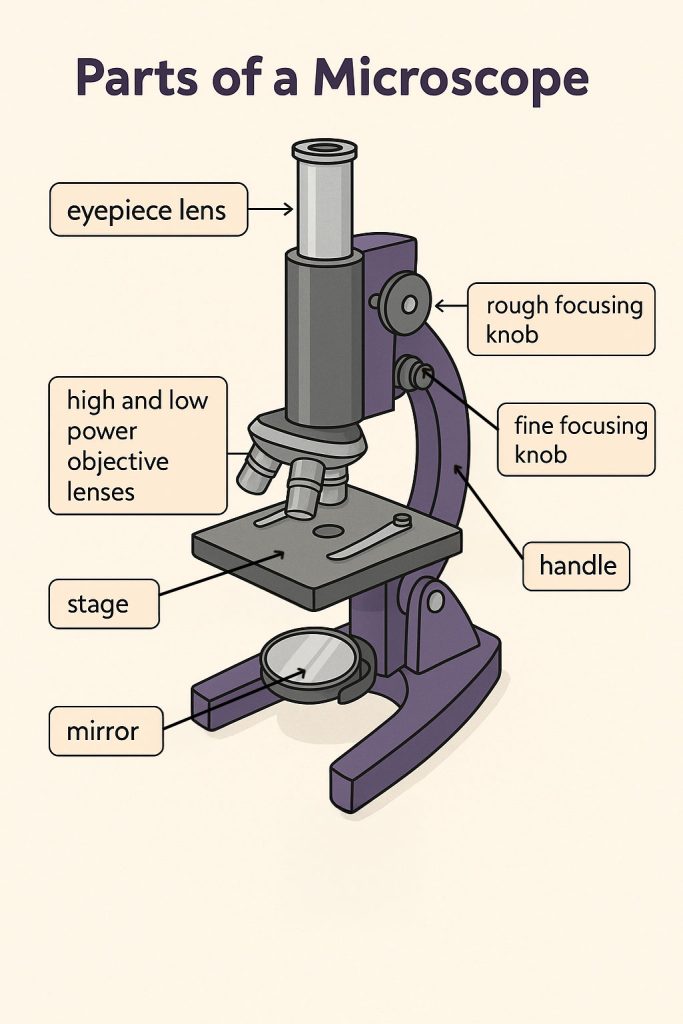
🕵️♀️ Meet the Microscope: Parts and Their Jobs
Here’s a breakdown of the main parts of a light microscope and what they do:
| 🔧 Part | 📝 Job |
|---|---|
| Eyepiece lens | The lens you look through (usually magnifies ×10) |
| Objective lenses | Lenses near the slide (e.g., ×4, ×10, ×40) — choose one for more detail |
| Stage | The platform where you place the slide |
| Clips | Hold the slide still |
| Mirror or Lamp | Sends light through the slide so you can see the image |
| Coarse focusing knob | Brings the object roughly into focus |
| Fine focusing knob | Sharpens the image to make it clear |
| Handle | Used to safely carry the microscope |
👣 Step-by-Step: Using a Microscope Safely
- Hold it properly: Carry the microscope using the handle.
- Set it up: Place it near a light source (but not direct sunlight).
- Prepare the slide: Place your slide on the stage and secure it with clips.
- Start small: Choose the lowest power objective lens (usually the shortest one).
- Focus it:
- Use the coarse knob to bring the lens close to the slide (but not touching).
- Then look through the eyepiece and use the fine knob to make it sharp.
- Zoom in: Want to see more detail? Switch to a higher power lens.
- Refocus as needed.
💡 TOP TIP: Always move the lens away from the slide while focusing to avoid cracking the glass.
🔍 Magnification: Making Things Look Bigger
Microscopes make small things look much bigger. That’s called magnification.
🧮 How to calculate magnification:
Magnification = Size of image ÷ Actual size of object
For example, if the image is 40 mm across and the real object is 0.01 mm:
Magnification = 40 ÷ 0.01 = ×4000
👁️🗨️ Resolution: Seeing Details Clearly
Resolution is the ability to see fine details clearly.
Even if something is magnified, if it looks blurry, the resolution is too low.
- High magnification + high resolution = 🔍 Clear & detailed image
- High magnification + low resolution = 🤨 Blurry and hard to see
✅ Quick Quiz (Test Yourself!)
- What part of the microscope do you look through?
- Which knob should you use for sharp focusing?
- Why should you not use sunlight with a microscope?
- What does magnification mean?
- What happens if the resolution is low?
